Posterior Predictive Checks for Bayesian Analyses fit in JAGS
ppcheck.RdA simple interface for generating a posterior predictive check plot for a JAGS analysis fit using jagsUI, based on the posterior distributions of discrepency metrics specified by the user and calculated and returned by JAGS (for example, sums of residuals). The user supplies the name of the discrepancy metric calculated for the real data in the argument observed, and the corresponding discrepancy for data simulated by the model in argument simulated. The posterior distributions of the two parameters will be plotted in X-Y space and a Bayesian p-value calculated.
pp.check(x, observed, simulated, xlab='Observed data', ylab='Simulated data',
main='Posterior Predictive Check', ...)Arguments
- x
A jagsUI object generated using the
jagsfunction- observed
The name of the parameter (as a string) representing the fit of the observed data (e.g. residuals)
- simulated
The name of the corresponding parameter (as a string) representing the fit of the new simulated data
- xlab
Customize x-axis label
- ylab
Customize y-axis label
- main
Customize plot title
- ...
Additional arguments passed to plot.default
Examples
#Analyze Longley economic data in JAGS
#Number employed as a function of GNP
#See ?jags for a more detailed example
#Get data
data(longley)
gnp <- longley$GNP
employed <- longley$Employed
n <- length(employed)
data <- list(gnp=gnp,employed=employed,n=n)
#Identify filepath of model file
modfile <- tempfile()
#Write model
#Note calculation of discrepancy stats fit and fit.new
#(sums of residuals)
writeLines("
model{
#Likelihood
for (i in 1:n){
employed[i] ~ dnorm(mu[i], tau)
mu[i] <- alpha + beta*gnp[i]
res[i] <- employed[i] - mu[i]
emp.new[i] ~ dnorm(mu[i], tau)
res.new[i] <- emp.new[i] - mu[i]
}
#Priors
alpha ~ dnorm(0, 0.00001)
beta ~ dnorm(0, 0.00001)
sigma ~ dunif(0,1000)
tau <- pow(sigma,-2)
#Derived parameters
fit <- sum(res[])
fit.new <- sum(res.new[])
}
", con=modfile)
#Set parameters to monitor
params <- c('alpha','beta','sigma','fit','fit.new')
#Run analysis
out <- jags(data = data,
inits = NULL,
parameters.to.save = params,
model.file = modfile,
n.chains = 3,
n.adapt = 100,
n.iter = 1000,
n.burnin = 500,
n.thin = 2)
#>
#> Processing function input.......
#>
#> Done.
#>
#> Compiling model graph
#> Resolving undeclared variables
#> Allocating nodes
#> Graph information:
#> Observed stochastic nodes: 16
#> Unobserved stochastic nodes: 19
#> Total graph size: 126
#>
#> Initializing model
#>
#> Adaptive phase, 100 iterations x 3 chains
#> If no progress bar appears JAGS has decided not to adapt
#>
#>
#> Burn-in phase, 500 iterations x 3 chains
#>
#>
#> Sampling from joint posterior, 500 iterations x 3 chains
#>
#>
#> Calculating statistics.......
#>
#> Done.
#Examine output summary
out
#> JAGS output for model '/tmp/RtmpWkPEqM/fileaa5643eba4c', generated by jagsUI.
#> Estimates based on 3 chains of 1000 iterations,
#> adaptation = 100 iterations (sufficient),
#> burn-in = 500 iterations and thin rate = 2,
#> yielding 750 total samples from the joint posterior.
#> MCMC ran for 0 minutes at time 2026-01-29 15:20:57.214734.
#>
#> mean sd 2.5% 50% 97.5% overlap0 f Rhat n.eff
#> alpha 51.825 0.737 50.315 51.835 53.335 FALSE 1.000 1.000 750
#> beta 0.035 0.002 0.031 0.035 0.038 FALSE 1.000 1.001 750
#> sigma 0.720 0.158 0.488 0.692 1.076 FALSE 1.000 1.005 750
#> fit -0.020 2.932 -5.756 -0.006 5.922 TRUE 0.501 0.999 750
#> fit.new 0.039 2.871 -5.191 -0.077 6.042 TRUE 0.483 1.006 369
#> deviance 33.338 2.941 30.012 32.466 40.361 FALSE 1.000 1.002 750
#>
#> Successful convergence based on Rhat values (all < 1.1).
#> Rhat is the potential scale reduction factor (at convergence, Rhat=1).
#> For each parameter, n.eff is a crude measure of effective sample size.
#>
#> overlap0 checks if 0 falls in the parameter's 95% credible interval.
#> f is the proportion of the posterior with the same sign as the mean;
#> i.e., our confidence that the parameter is positive or negative.
#>
#> DIC info: (pD = var(deviance)/2)
#> pD = 4.3 and DIC = 37.664
#> DIC is an estimate of expected predictive error (lower is better).
#Posterior predictive check plot
pp.check(out, observed = 'fit', simulated = 'fit.new')
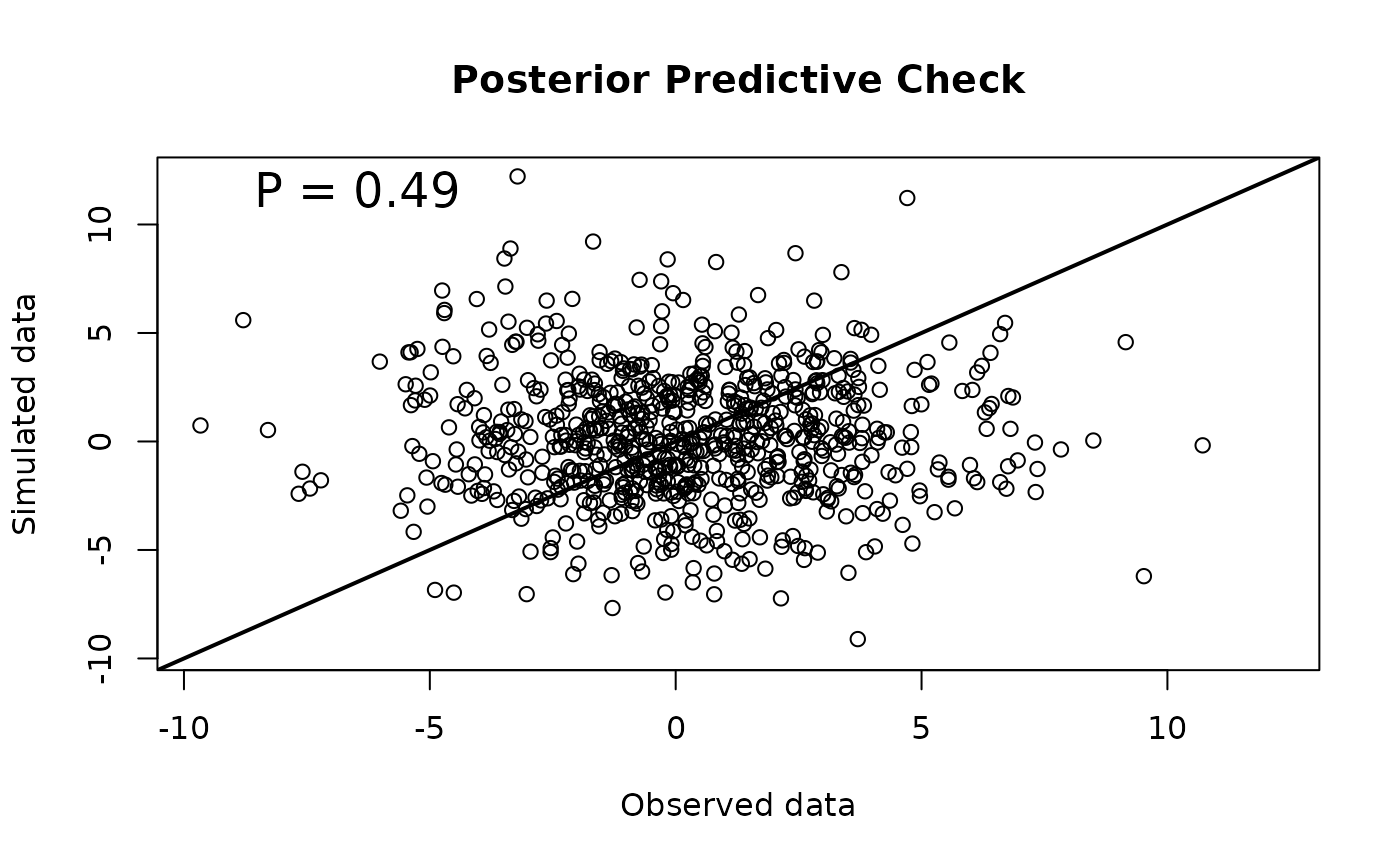 #> [1] 0.4946667
#> [1] 0.4946667